The professional activities are performed by specialists from various sectors (not only geographers), typically to perform land surveying, land areas and routes definition. Some real case studies from the most relevant sectors are presented hereafter.
Agriculture & Forest
The GPS Waypoints is being used in Agriculture for both planning and monitor cultivated areas. It is used to measure crops areas in order to estimate production (create Manual Polygons), measure and plot new tubing layouts of sugar maple trees pipes (create Manual Paths), identify and classify the infested trees on olive groves or cork farms (Use custom tags and photo attachment).
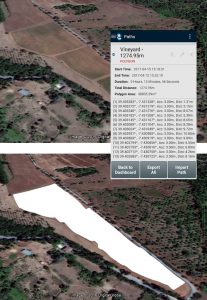 Define and measure a new plantation area Define and measure a new plantation area |
 Sugar Maple Trees Sugar Maple Treespipe planning |
 Olive Trees infestation monitoring Olive Trees infestation monitoring |
Real Estate & Construction
The tool is used by Real Estate owners, evaluators or buyers in order to measure land properties, determining boundaries and areas, for planning and valuation purposes. The user must collect sequential points of the land surroundings and close the path to build a polygonal area.
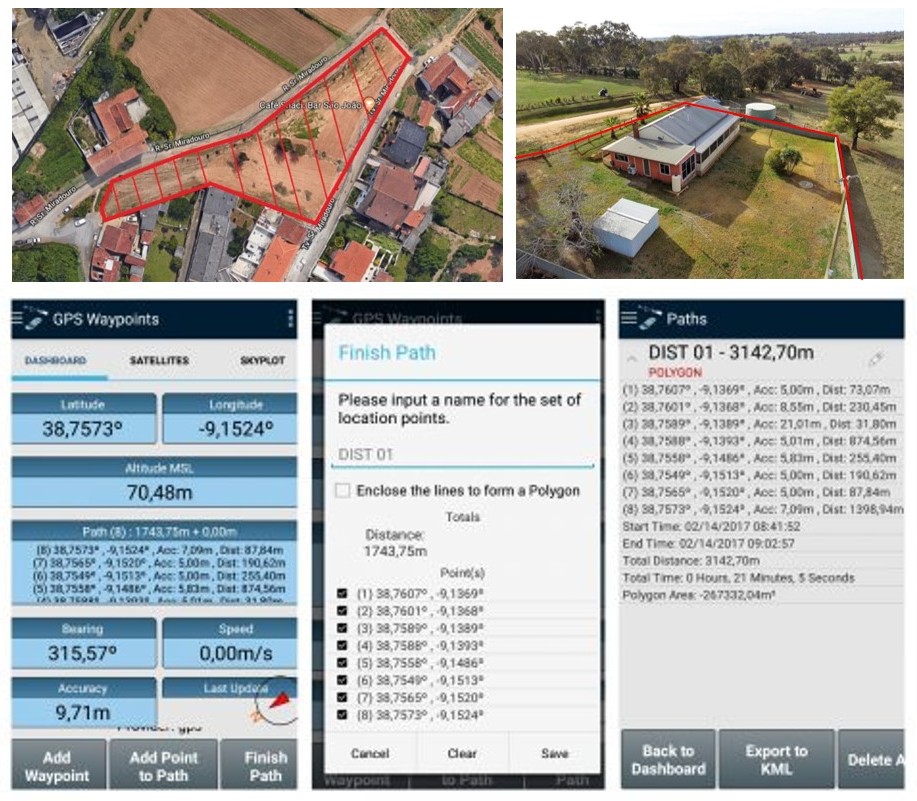 |
 |
|
| Define and measure a land property area for sale or land-use change | Acquire precise control points connected with an external precision RTK receiver for integrating with total station measurements |
The tool is also used in urban planning to support land use mapping activities. The user collects the points on the field, tags them using his classification system and exports the results to validate the thematic classes or determine the mapping accuracy.
The combination of conventional survey instruments and high precision GPS is an advanced use case of GPS Waypoints. It can support topographic surveys for construction sites without requiring the know-how of a GNSS specialist.
Infrastructures
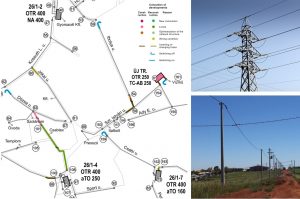
The tool can be used for planning network infrastructures and maintaining them for producing incident report data. Two known infrastructure use cases are the road pavement maintenance and the planning of electric distribution systems, as depicted in the figures below.
 |
 |
|
| Road pavement classification for maintenance | Planning medium-voltage and low-voltage distribution systems |
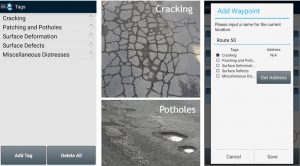
The road pavement maintenance professionals need to evaluate and classify the road status. They can identify pavements distresses with exact coordinates of the failures and associate a tag based on their own classification model. The model can be adapted for each country, using different levels of detailed. For instance, pavement distress model for asphalt concrete surfaces could be as simple as:
-
Cracking
-
Patching and Potholes
-
Surface Deformation
-
Surface defects
-
Miscellaneous Distresses
The planning of electric distribution systems needs to define in Autocad the new the medium-voltage and low-voltage networks and change the existing ones. The GPS Waypoints is used to collect the waypoints on the field, export them to KML for later conversion to Autocad (automatic export feature to Autocad will soon be available). The collected waypoints will support the drawing of new planning diagrams.
Emergencies
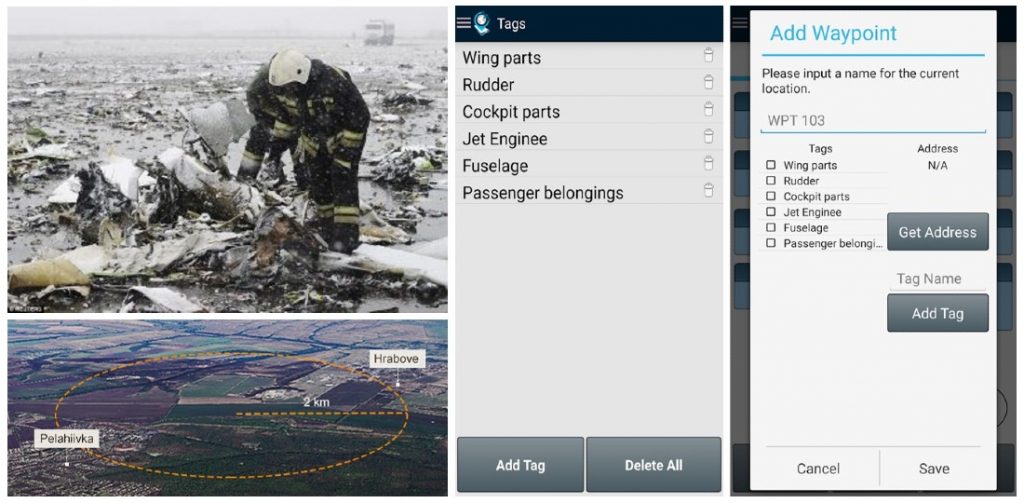
GPS Waypoints can help emergencies to map objects or incidents in a disaster area or eventually to support some disaster response activities.
 |
 |
|
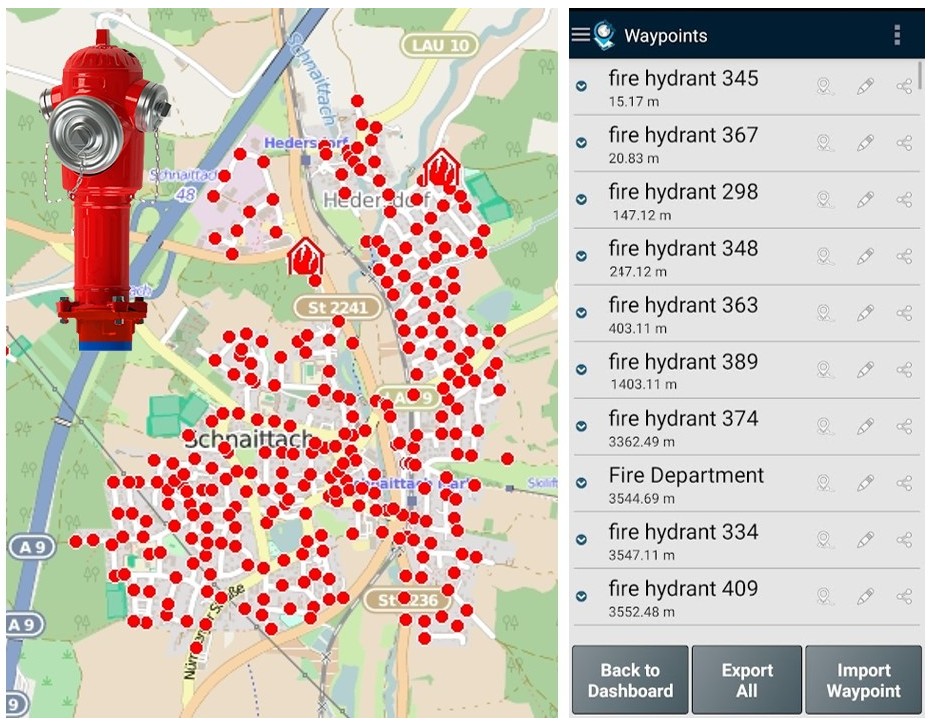
| Disaster debris mapping | Locate the nearest fire hydrants from my area |
It can be usefull for mapping the object founds on post-disaster area since it allows collecting position and classifying the wreckage and other objects found. The application becomes particular relevant in activities that need to be fastly performed in a wide area, typically involving volunteers.
Another use case is to import rescue Points, such as the hydrant locations from a fire department. During the response time, the tool can support an emergency agent (e.g fireman) to get the nearest ones (sort Points by proximity) and obtain directions to each of them.